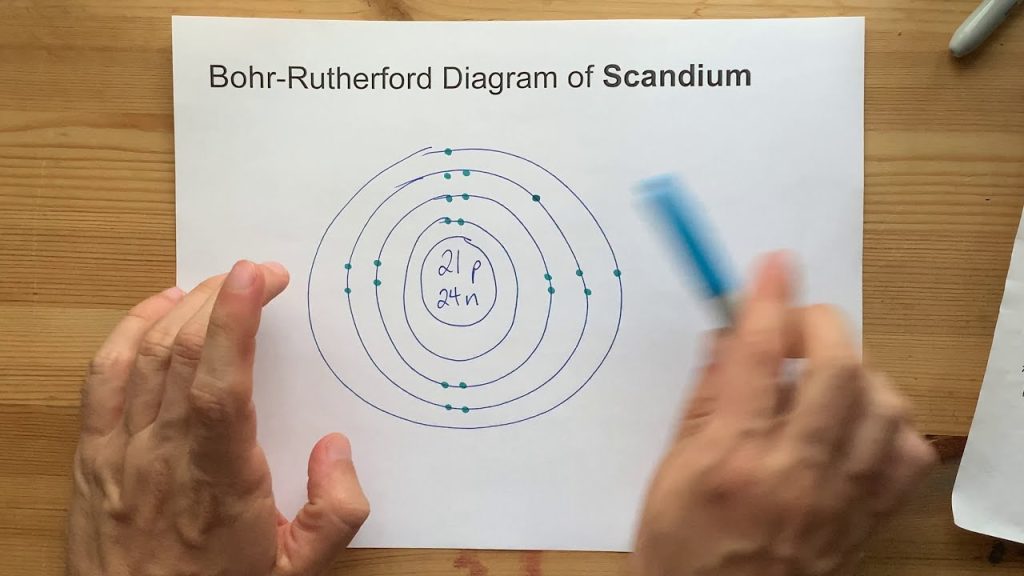
The electron configuration of Scandium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1. Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21.
Scandium is a silvery-white transition metal commonly found in various minerals. It is relatively rare and is usually obtained as a byproduct of processing other minerals such as Uranium and Tantalum. Scandium’s electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1.
This means that it has one electron in its outermost energy level. Scandium is known for its high melting point, ductility, and corrosion resistance. It is widely used in the aerospace industry, where its light weight and strength make it an ideal material for aircraft components. In recent years, Scandium has also gained attention for its potential use in fuel cell technology.
What Is Scandium
Scandium has an electron configuration of [Ar] 3d¹ 4s². It is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. Due to its lightweight and strength, Scandium is often used in alloys with other metals.
Elementary Information
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol ‘Sc’ and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic transition metal and belongs to the rare earth element group. Scandium has a melting point of 1541 °C and a boiling point of 2836 °C. It is similar to aluminum and is found in the earth’s crust in minerals such as thortveitite, bazzite, and euxenite.
Historical Background
Scandium was discovered by a Swedish chemist named Lars Fredrik Nilson in 1879. Nilson found scandium in the minerals euxenite and gadolinite. However, the element was not isolated in its pure form until 1937 due to its difficulty separating it from other elements. During the early 1900s, scandium was believed to have radioactive properties due to its presence in radioactive minerals. However, it was later found that scandium is not a radioactive element. Scandium has various applications in the aerospace, sports equipment, and electronics industries. Its unique properties make it a vital component in alloy manufacturing, particularly in producing high-performance sports equipment like bicycle frames.
Scandium Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of scandium is [Ar] 3d1 4s2. This means there are two electrons in the outer shell and one unpaired electron in the 3d orbital. The unpaired electron in the 3d orbital gives scandium unique properties, such as its ability to form stable compounds with high melting points. Scandium is also a good conductor of electricity and has a high heat tolerance, making it useful in producing various alloys. Overall, scandium has proven to be a versatile element with a wide range of applications. As further research is conducted, its potential uses are expected to expand even further.
What Is Electron Configuration
Scandium’s electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1. This means that in its ground state, scandium has one electron in its 3d subshell and nine electrons in its outermost energy level. Scandium’s electron configuration makes it a unique transitional metal with various applications.
What Is Electron Configuration?
At its most basic level, electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons within an atom. This arrangement plays a crucial role not only in the atom’s chemical behavior but also in its physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and conductivity.
Definition
Electron configuration is defined as the distribution of electrons of an atom into its orbitals. In simpler terms, it is how the electrons are arranged in an atom. This arrangement is based on the energy levels of the electrons and the maximum number of electrons that can occupy each level. The first energy level can hold up to two electrons, while the second can hold up to eight.
Importance
Understanding electron configuration is essential in the study of chemistry and physics. It helps predict the chemical reactions an atom is likely to undergo and how it will interact with other atoms. For instance, elements with similar electron configurations tend to have similar chemical properties. This is because they have the same number and arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level, known as the valence shell. Scandium, for example, has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1. This means it has one valence electron in the 3d orbital, making it a transition metal with unique chemical properties. In summary, while electron configuration may seem like a simple concept, it plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of atoms and their interactions with other atoms. The arrangement of electrons within an atom helps in predicting its chemical and physical properties, making it an essential concept in the field of science.
How To Write Electron Configuration Of Scandium
Writing the electron configuration of scandium involves understanding the principles of quantum mechanics. Scandium has 21 electrons, so its electron configuration can be represented as 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p6 4s² 3d¹.
Scandium, with an atomic number of 21, is a chemical element that has garnered interest owing to its versatile industrial applications. Its electron configuration can be defined as 1s2262621. Here’s a step-by-step procedure for writing the electron configuration of Scandium.
Step-by-step Procedure
-
First, identify the atomic number of Scandium, which is 21.
-
Next, write the electronic configuration for the first 18 electrons, which recursively fill up the first three energy levels. The electronic configuration for Scandium’s first 18 electrons will be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
-
Then, fill up the fourth energy level with the remaining 3 electrons. The electrons will fill up as 4s2 3d1.
-
Finally, ensure that the total number of electrons written equals the atomic number of the element, which is 21 for Scandium.
Orbital Diagram
Alternatively, you can also represent the electron configuration of Scandium using an orbital diagram, which visually represents the distribution of electrons in different energy levels. Here’s a simple orbital diagram for Scandium:
|
1s |
↑↓ |
|
2s |
↑↓ |
|
2p |
↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
|
3s |
↑↓ |
|
3p |
↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ |
|
4s |
↑↓ ↑↓ |
|
3d |
↑↓ ↑ ↑↑ |
In the orbital diagram, each box represents an orbital, and the arrow in each box denotes an electron spin, with the upward and downward arrows representing opposite electron spins. In conclusion, the electron configuration of Scandium has a unique arrangement of electrons that makes it a fascinating element to study and observe. With industrial applications ranging from aerospace to sports equipment, the extensive use of Scandium only adds to its intrigue.
What Is The Ground State Electron Configuration Of Scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a transition metal and has three valence electrons. The electron configuration of scandium is the arrangement of its electrons in its atomic orbitals. The ground state electron configuration of scandium can be determined using the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons will first occupy the lowest available energy levels.
Explanation
Scandium has 21 electrons. The first two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, the next two electrons occupy the 2s orbital, and the next six electrons occupy the 2p orbitals. The next two electrons occupy the 3s orbital, leaving nine electrons to occupy the 3p orbitals. The configuration of the last five electrons can be written as 3d1 4s2. Since the 4s orbital is lower in energy than the 3d orbital, the electrons in the 4s orbital are filled first, followed by the 3d orbital. As a result, the ground state electron configuration of scandium is [Ar] 3d1 4s2.
Notation
In electron configuration notation, the number of electrons in each energy level is listed, followed by the letter of the orbital and a superscript of the number of electrons in that orbital. For example, the ground state electron configuration of scandium can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1.
Summary
-
Scandium has 21 electrons, and the electron configuration is the arrangement of its electrons in its atomic orbitals.
-
The Aufbau principle determines the ground state electron configuration of scandium.
-
Scandium’s ground state electron configuration is [Ar] 3d1 4s2.
-
Electron configuration notation lists the number of electrons in each energy level, followed by the letter of the orbital and a superscript of the number of electrons in that orbital.
Understanding the electron configuration of scandium is important in understanding its chemical behavior and reactivity with other elements. Scandium has unique properties due to its electron arrangement, making it useful for various applications in industry and research.
Why Scandium Is A Transition Metal
Scandium’s electron configuration is [Ar]3d14s2, which means that its outermost orbitals include both d and s subshells of the third shell, making it a transition metal.
Properties And Characteristics
Scandium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is relatively rare in the Earth’s crust. It is a reactive element that easily forms compounds with other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon.
Scandium also exhibits unique properties that make it useful in a range of industrial applications. For example, it has a high melting point (1541°C) and a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can absorb and release large amounts of energy without changing temperature.
Another interesting characteristic of scandium is its magnetic behavior. In its pure form, it is not magnetic, but when it is alloyed with other metals like aluminum or iron, it can become strongly magnetic.
Examples
Scandium is used in various applications thanks to its unique properties and characteristics. Some common examples include:
-
Aluminum-scandium alloys are used in aerospace applications to make lightweight, strong components for aircraft and satellites.
-
Scandium iodide is used in high-intensity lamps and as a crystal stabilizer in lasers.
-
Scandium oxide is used as a high-strength material in ceramic applications.
Overall, scandium’s status as a transition metal gives it many of its unique properties and characteristics and makes it a valuable element in a range of industrial applications.
What Are The Applications Of Scandium
Due to its unique properties, including its electron configuration, Scandium has several applications. It is used in aerospace, sports equipment, and even the production of high-intensity lamps. Its lightweight and strength make it an attractive material for use in various industries.
Scandium is a rare earth metal with unique properties that make it useful in various industries. One of the most crucial aspects of scandium is its electron configuration, which makes it a valuable addition to different materials. It has four valence electrons, which means it can form stable compounds with other elements. While scandium is still relatively rare, its applications have expanded rapidly in recent decades. In this article, we will focus on the applications of Scandium with subheadings such as Aerospace Industry, Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, and Sports Equipment and discuss how Scandium has been making its mark with its valuable properties and applications.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry has a massive demand for materials with high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Scandium’s electron configuration enables it to blend easily with aluminum alloys, making it a suitable candidate for lightweight, high-strength alloys for aerospace applications. Scandium-aluminum alloys reduce the aircraft’s weight while maintaining strength and structural integrity. Scandium-enhanced alloys have already found applications in Russian and Ukrainian fighter jets and have also been tested in American and European aircraft models.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells require high-temperature materials that can withstand oxidizing environments and maintain stability during cyclic thermal strains. Scandium-stabilized zirconia is a well-known oxide ion conductor that can be used for high-temperature applications like solid oxide fuel cells. It acts as an oxygen ion vacancy stabilizer, which improves ionic conductivity and lowers operating temperatures. Scandium-stabilized zirconia has shown potential for the development of high-performance solid oxide fuel cells that can provide efficient, reliable, and clean energy for both residential and commercial use.
Sports Equipment
Scandium’s high strength and low density make it an essential material in sports equipment. Scandium alloy golf clubs, tennis rackets, and baseball bats have become increasingly popular because they offer superior performance, comfort, and durability. Scandium’s unique properties also enable the production of lighter, stiffer, and more durable bike frames that can withstand the harsh demands of professional cycling. In conclusion, Scandium’s electron configuration and unique properties have made it a valuable addition to various industries. Its applications extend from aerospace, energy, sports equipment, and beyond, making it a critical metal for modern technological progress. Collaborative research and innovation in scandium-based materials continue to hold promise for developing high-performance materials for use in many fields.
What Are Some Interesting Facts About Scandium
What are some Interesting Facts about Scandium?
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic transition metal that belongs to the group 3 of the periodic table. Scandium has many interesting facts that make it unique among other elements. Let’s look at some of them:
Discovery
Scandium was discovered in 1879 by Lars Fredrik Nilson, a Swedish chemist. He found the element in the minerals euxenite and gadolinite. The discovery of scandium filled a gap in the periodic table of elements and opened up new research areas.
Abundance
Scandium is a relatively rare element in the Earth’s crust. It is only the 50th most abundant element on Earth, making up only 22 parts per million (ppm) of the crust. Scandium is also found in small amounts in some minerals, including thortveitite, bazzite, and kolbeckite. The low abundance of scandium makes it a costly element.
Price
Due to its scarcity, scandium is one of the most expensive metals on Earth. In fact, the cost of scandium is around 100 times higher than that of aluminum. The price of scandium varies depending on factors such as the supply-demand ratio, market dynamics, and the cost of production. Despite its high cost, scandium has many uses in various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and sports equipment.
To sum up, scandium is a rare and costly metal with many interesting properties. Its discovery contributed greatly to the development of the periodic table of elements, and its unique properties make it a valuable resource for various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions On Scandium Electron Configuration
How Do You Write The Electron Configuration For Scandium?
The electron configuration for scandium is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹.
Why Is Scandium Electron Configuration 2 8 9 2?
Scandium has 21 electrons arranged in a 2-8-9-2 configuration. The first two electrons are in the 1s subshell, the next eight are in the 2s, and 2p subshells, nine are in the 3s, and 3p subshells, and the last two are in the 3d subshell.
This gives scandium a partially filled sublevel, making it a transition metal.
What Element Has An Electron Configuration Of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4?
The element with an electron configuration of 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4 is sulfur, with 16 electrons in total.
What Is The Element With An Electron Configuration Of 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1?
The element with an electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 is Scandium (Sc).
Conclusion
Since its discovery, the scandium electron configuration has been a topic of interest. Knowing the arrangement of electrons in an atom helps us understand its properties, including its chemical behavior and physical characteristics. Scandium is a unique element with an electron configuration that makes it useful in various industries, including aerospace and medicine.
Keep exploring the world of scandium and its electron configuration for a better understanding of the periodic table.