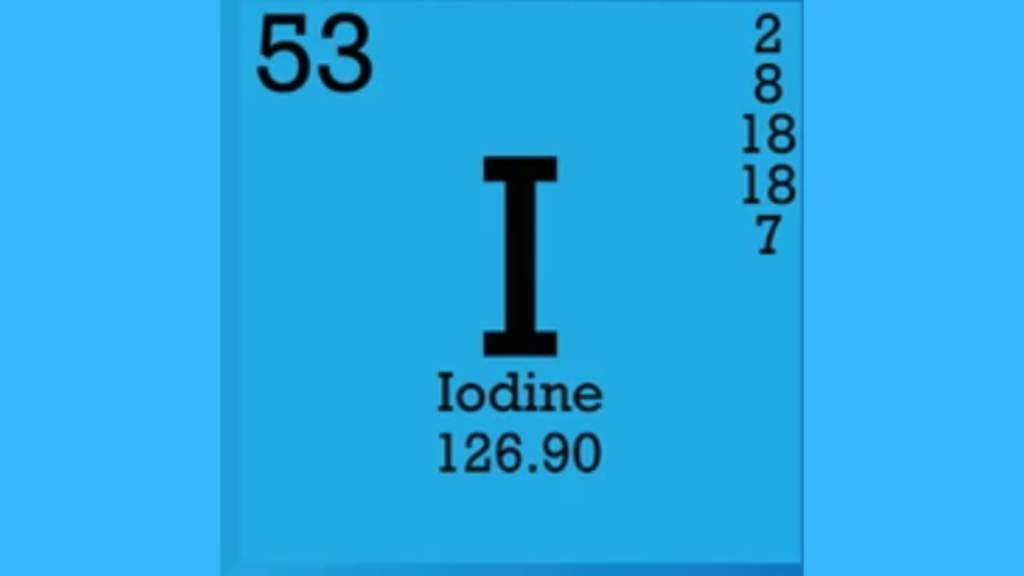
Iodine has seven valence electrons. It belongs to Group 17 in the periodic table.
Iodine is a crucial element in chemistry and essential for human health. It is part of the halogen group, which includes elements like fluorine and chlorine. Iodine’s seven valence electrons make it highly reactive, especially with metals. This reactivity is why iodine forms compounds easily, such as iodides.
Iodine is vital for thyroid function and influences metabolism and overall health in the human body. Its deficiency can lead to health issues like goiter. Understanding iodine’s chemical properties and biological importance helps in various scientific and medical fields. Knowing the number of valence electrons aids in predicting iodine’s behavior in chemical reactions.
Introduction To Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. They play a key role in chemical reactions, and understanding them helps us predict chemical behavior.
Each element has a unique number of valence electrons. These electrons determine how an element will react.
For example, iodine is a fascinating element. It’s important in many chemical processes.
Importance In Chemistry
Valence electrons are vital in chemical bonding. They decide how atoms bond with each other.
Atoms form bonds to become stable. Valence electrons help achieve this stability.
Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of valence electrons.
Understanding valence electrons can explain why certain elements react. It also tells us how they form compounds.
Basic Concepts
Each element’s position in the periodic table reveals its valence electrons. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
For example, iodine is in Group 17. All elements in this group have seven valence electrons.
| Element | Group | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Iodine (I) | 17 | 7 |
- Valence electrons determine reactivity.
- Atoms strive for a full valence shell.
- Elements in the same group have similar properties.
To sum up, understanding valence electrons is crucial. They help us make sense of the chemical world.
Iodine In The Periodic Table
Iodine is an essential chemical element with unique properties and a significant role in chemistry. This section explains its position in the periodic table.
Group And Period
Iodine is in Group 17 of the periodic table, which includes elements like fluorine and chlorine.
Iodine is located in Period 5. Elements in the same period have the same number of atomic orbitals.
Atomic Structure
Iodine has an atomic number of 53, which means it has 53 protons and electrons arranged in different shells.
Here is a simple table showing iodine’s electron configuration:
| Shell | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| K | 2 |
| L | 8 |
| M | 18 |
| N | 18 |
| O | 7 |
The outermost shell, shell O, has 7 valence electrons, which play a key role in chemical reactions.
Determining Valence Electrons
Understanding an element’s valence electrons is crucial in chemistry. These electrons determine how an element reacts with others. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom. They are found in the highest energy level or shell.
Electron Configuration
Iodine has an atomic number of 53. This means it has 53 protons and, in a neutral atom, 53 electrons. The electron configuration of iodine is:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p5
This configuration shows the arrangement of electrons in various shells and subshells. The fifth shell has the highest energy level.

Valence Shell
The valence shell is the outermost electron shell of an atom. The valence shell is the fifth shell for iodine, containing the 5s2 5p5 electrons.
To determine the number of valence electrons, look at the electrons in the outermost shell:
| Shell | Subshell | Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | s | 2 |
| 5 | p | 5 |
Adding these electrons gives iodine seven valence electrons, making it a member of the halogen group, which is known for having seven valence electrons.
Knowing the number of valence electrons helps predict iodine’s chemical behavior. It also allows chemists to understand how iodine bonds with other elements.
Iodine’s Electron Configuration
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. Understanding its electron configuration can help explain its chemical behavior. Let’s break down iodine’s electron configuration in detail.
Orbital Notation
Orbital notation is a way to show the arrangement of electrons in an atom. Each orbital can hold up to two electrons. These electrons are represented by arrows pointing up and down.
Iodine has 53 electrons. Its electron configuration can be written as:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁵
In this notation:
- 1s²: 2 electrons in the 1s orbital
- 2s² 2p⁶: 8 electrons in the second energy level
- 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰: 18 electrons in the third energy level
- 4s² 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰: 18 electrons in the fourth energy level
- 5s² 5p⁵: 7 electrons in the fifth energy level
Energy Levels
Electrons are arranged in energy levels around the nucleus. Each level can hold a certain number of electrons. The first level can hold 2 electrons. The second can hold 8 electrons. The third can hold 18 electrons.
Iodine has electrons in five energy levels:
| Energy Level | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 18 |
| 4 | 18 |
| 5 | 7 |
The outermost energy level of iodine is the fifth level. This level has 7 electrons. These are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are important for chemical reactions.
Iodine’s Valence Electrons
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. It belongs to the halogen group and is well-known for its role in nutrition and medicine. Understanding the number of valence electrons iodine has is crucial for grasping its chemical behavior and reactivity.
Count And Significance
Iodine has seven valence electrons located in the outermost shell of the atom. These electrons determine how iodine interacts with other elements and play a key role in forming chemical bonds.
The presence of seven valence electrons makes iodine highly reactive. It seeks to gain one more electron to complete its outer shell. This makes iodine a good oxidizing agent. It can easily form compounds with other elements. The reactivity of iodine is essential in various chemical reactions.
Comparison With Other Halogens
| Element | Valence Electrons | Reactivity |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorine | 7 | Very High |
| Chlorine | 7 | High |
| Bromine | 7 | Moderate |
| Iodine | 7 | Low |
| Astatine | 7 | Very Low |
All halogens have seven valence electrons. This common feature makes them very reactive. Fluorine is the most reactive, while astatine is the least. Iodine’s reactivity is lower than fluorine and chlorine but higher than astatine.
The decreasing reactivity trend is due to the increasing atomic size. As the atomic size increases, the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, making it harder for the atom to attract additional electrons.
Chemical Properties Of Iodine
Iodine is an essential element with unique chemical properties. It has a distinct place in the periodic table. Understanding iodine’s chemical properties helps us understand its behavior in reaction. Let’s explore these properties in detail.
Reactivity
Iodine is less reactive than other halogens like fluorine or chlorine. It reacts with some metals and nonmetals. When iodine reacts with metals, it forms iodides. For example, potassium iodide forms when iodine reacts with potassium.
Iodine also reacts with hydrogen gas to form hydrogen iodide (HI). This reaction needs heat or a catalyst to proceed. Iodine can oxidize, meaning it can gain electrons during reactions.
Bond Formation
Iodine has seven valence electrons. It can form single bonds with other atoms. In many compounds, iodine forms a single bond with hydrogen, as in hydrogen iodide. Iodine can also form bonds with carbon in organic molecules.
Iodine can form multiple bonds in more complex molecules. An example is iodine pentafluoride (IF5), where iodine forms five single bonds with fluorine atoms. This versatility makes iodine a key player in many chemical reactions.
Applications Of Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with a variety of uses. It plays a vital role in both medical and industrial fields. Understanding these applications can help us appreciate their importance in our daily lives.
Medical Uses
Iodine is essential in the medical field. It is a key component in disinfectants and antiseptics. Doctors use iodine solutions to clean wounds and prevent infections. Iodine is also critical for thyroid health. It helps produce thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism.
Radioactive iodine is used in medical imaging. It helps diagnose and treat thyroid disorders. Patients take a small dose of radioactive iodine, which doctors then track using imaging equipment. This allows doctors to see how the thyroid functions.
Industrial Uses
Iodine is valuable in various industries. It is used in producing iodized salt, which helps prevent iodine deficiency in populations and is essential for maintaining thyroid health.
The chemical industry uses iodine as a catalyst. It helps speed up chemical reactions. Iodine is also used to produce dyes, inks, and photographic chemicals. These applications make it a versatile element in manufacturing.
Iodine compounds are used in water purification. They help kill bacteria and other harmful organisms, making drinking water safe. This is particularly important in areas without access to clean water. Google maps
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Valence Electrons In Iodine?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom. In iodine, they determine how it bonds with other elements. Iodine has seven valence electrons. These electrons play a crucial role in chemical reactions and bonding.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Iodine Have?
Iodine’s outermost shell contains seven valence electrons, which are crucial for its chemical properties and make it highly reactive.
Why Is Iodine Reactive?
Iodine is reactive because it has seven valence electrons. It needs one more to complete its outer shell. This makes iodine eager to form bonds. Its reactivity is vital in chemical reactions.
What Group Is Iodine In The Periodic Table?
Iodine is in Group 17 of the periodic table, also known as the halogens. Elements in this group have seven valence electrons. They are highly reactive and form similar types of bonds.
Conclusion
Understanding iodine’s seven valence electrons is crucial for grasping its chemical behavior. These electrons play a key role in reactions and bonding, which helps in fields like chemistry, medicine, and industry. Stay informed about such elements to enhance your knowledge and applications in various scientific domains.