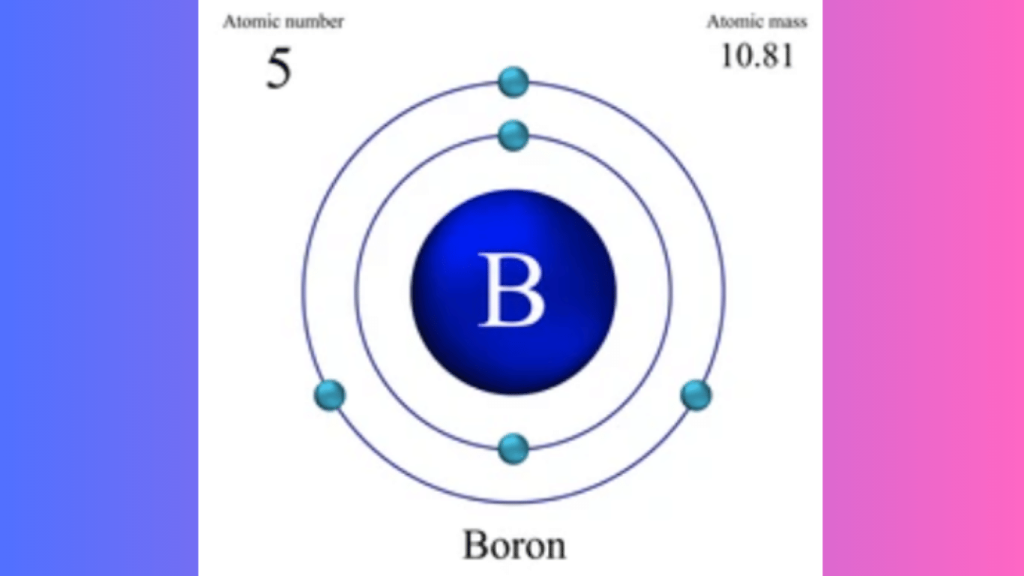
Boron has three valence electrons. These electrons reside in the second energy level.
Boron, with the atomic number 5, belongs to group 13 of the periodic table. It is a metalloid exhibiting properties of both metals and non-metals. Valence electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding and reactivity. With three valence electrons, boron can form stable covalent bonds.
This makes it a key element in various compounds and industrial applications. Understanding boron’s electron configuration helps in predicting its chemical behaviour. Its unique properties make it essential in fields like electronics, agriculture, and materials science. Boron compounds, such as boric acid and borates, are widely used in everyday products. This versatility highlights the importance of knowing its valence electrons.
Introduction To Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. They play a key role in determining how atoms interact and bond with each other, and understanding them is crucial in chemistry.
Definition And Importance
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. They determine an element’s chemical properties. For example, Boron has three valence electrons.
These electrons are involved in forming chemical bonds. The more valence electrons an atom has, the more bonds it can form. This makes valence electrons very important in chemistry.
Role In Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding occurs when atoms share or transfer valence electrons, creating stable molecules. With three valence electrons, Boron can form three bonds with other atoms.
There are different types of chemical bonds, including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Valence electrons determine the type and strength of these bonds.
For example, in a covalent bond, atoms share valence electrons. This sharing creates a strong bond that holds molecules together.
| Element | Valence Electrons | Common Bonds Formed |
|---|---|---|
| Boron | 3 | 3 Covalent Bonds |
| Carbon | 4 | 4 Covalent Bonds |
| Oxygen | 6 | 2 Covalent Bonds |
Basics Of Boron
Boron is a fascinating element with unique properties. It plays a crucial role in various scientific fields. Understanding boron’s basics helps us appreciate its importance. Let’s delve into its atomic structure and position in the periodic table.
Atomic Structure
Boron has an atomic number of 5. This means it has 5 protons in its nucleus. Boron also has 5 electrons orbiting around the nucleus. These electrons are arranged in two shells. The first shell holds 2 electrons, and the second shell holds 3 electrons.
Here’s a simple representation of boron’s atomic structure:
| Shell | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| First Shell | 2 |
| Second Shell | 3 |
Boron has 3 electrons in its outermost shell, which are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are important for chemical bonding.
Position In The Periodic Table
Boron is the first element in Group 13 of the periodic table. It is also placed in the second period, which means it is in the second row of the table.
Here are some key points about Boron’s position:
- Group: 13
- Period: 2
- Symbol: B
- Atomic Number: 5
Boron is in Group 13 and shares some properties with aluminium, gallium, indium, and thallium. Understanding its position helps us predict its behaviour in chemical reactions.
Electron Configuration Of Boron
The electron configuration of Boron is vital to understanding its chemical properties. Knowing how many valence electrons Boron has helps in various scientific applications. This section will explore the electron configuration of Boron through the Bohr Model and the Quantum Mechanical Model.
Bohr Model
The Bohr Model is a simple way to represent an atom. It shows electrons orbiting the nucleus in defined paths.
In this model, Boron has a total of 5 electrons. These are arranged in two energy levels:
- First energy level: 2 electrons
- Second energy level: 3 electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell are the valence electrons. For boron, there are 3 valence electrons at the second energy level.
Quantum Mechanical Model
The Quantum Mechanical Model offers a more accurate representation of an atom. It uses complex shapes of orbitals where electrons are likely to be found.
Boron’s electron configuration is written as 1s2 2s2 2p1 in this model. This means:
- Two electrons in the 1s orbital
- Two electrons in the 2s orbital
- One electron in the 2p orbital
Even with this complex model, Boron still has 3 valence electrons. These are found in the 2s and 2p orbitals.
Understanding these models helps in the study of chemical reactions and bonding. The valence electrons play a key role in these processes.
Determining Valence Electrons
Determining the number of valence electrons is crucial in chemistry. It helps us understand how elements bond and react. Let’s learn how to find the valence electrons in Boron.
Steps To Identify
Follow these simple steps to identify Boron’s valence electrons:
- Find Boron’s atomic number. It is 5.
- Determine its electron configuration. Boron’s electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p1.
- Look at the outermost shell. The outer shell has 2s and 2p electrons.
- Count the electrons in the outer shell. Boron has 3 valence electrons.
Common Misconceptions
Many people make mistakes when identifying valence electrons. Here are some common misconceptions:
- Misconception: All electrons are valence electrons.
- Fact: Only the outermost shell’s electrons are valence electrons.
- Misconception: Boron has 5 valence electrons.
- Fact: Boron only has 3 valence electrons.
- Misconception: Inner shell electrons can be valence electrons.
- Fact: Valence electrons are only in the outermost shell.
Boron’s Valence Electrons
Boron is an essential element in chemistry and materials science. Understanding its valence electrons, which determine how an element reacts with others, is crucial. Let’s explore the number of valence electrons Boron has and their impact on reactivity.
Number Of Valence Electrons
Boron, with atomic number 5, belongs to Group 13 of the periodic table. It has three valence electrons in its outer shell.
| Element | Atomic Number | Group | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron | 5 | 13 | 3 |
These three valence electrons play a key role in their chemical behaviour.
Impact On Reactivity
Valence electrons determine an element’s reactivity. Boron’s three valence electrons make it versatile in forming bonds. It can form covalent bonds with many elements.
- Chemical Bonding: Boron readily forms covalent bonds.
- Compounds: Boron compounds are essential in many industries.
- Semiconductors: Boron is used to make semiconductors.
Because of its valence electrons, Boron is valuable in various applications. Its ability to bond with other elements makes it unique.
Boron In Chemical Reactions
Boron is a fascinating element. It has only three valence electrons, which makes it quite reactive. Boron forms various compounds and bonds. Let’s delve into some examples.

Common Compounds
Boron forms many compounds. Here are a few:
- Boron Trifluoride (BF3): Used in organic synthesis.
- Boric Acid (H3BO3): Common in antiseptics.
- Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4): A powerful reducing agent.
Each of these compounds has unique properties. They are used in different industries.
Bonding Patterns
Boron tends to form covalent bonds. It shares electrons with other elements. Here are some bonding patterns:
| Compound | Bond Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Triangular Planar | Covalent | BF3 |
| Tetrahedral | Covalent | BH4– |
In boron trifluoride, boron forms three bonds. It creates a triangular planar shape. In borohydride, boron forms four bonds. This results in a tetrahedral shape.
Applications Of Boron
Boron, with its unique properties, finds applications across diverse fields. Its valence electrons make it a versatile element in both industrial and biological contexts. This section explores the various uses of boron in everyday life.
Industrial Uses
Boron is an essential element in many industries. It is critical for enhancing product performance and durability.
- Glass and Ceramics: Boron is used in glass and ceramics manufacturing. It improves durability and heat resistance.
- Detergents: In detergents, boron compounds enhance cleaning efficiency.
- Electronics: Boron is vital in semiconductor production, enhancing conductivity.
- Fibreglass: Boron strengthens fibreglass, making it more durable and reliable.
Biological Significance
Boron is crucial in industries and has significant biological roles. It contributes to the health and development of plants and animals.
- Plant Growth: Boron is essential for plant cell wall strength and development.
- Bone Health: Boron plays a role in maintaining bone health and calcium metabolism in humans.
- Brain Function: Boron influences cognitive functions and brain activity.
- Hormone Regulation: It helps regulate hormones, impacting overall health.
| Application | Importance |
|---|---|
| Glass and Ceramics | Improves durability and heat resistance |
| Detergents | Enhances cleaning efficiency |
| Electronics | Enhances conductivity |
| Fiberglass | Strengthens and improves reliability |
| Plant Growth | Essential for cell wall strength |
| Bone Health | Maintains bone health and calcium metabolism |
| Brain Function | Influences cognitive functions |
| Hormone Regulation | Impacts overall health |
Interesting Facts About Boron
Boron is a fascinating element with unique properties and a rich history. Let’s explore some interesting facts about boron under the following headings:
Historical Background
Boron was first isolated in 1808 by French chemists. The element’s name comes from the Arabic word “burqa” and the Persian word “burh, ” which means borax.
Borax was used in ancient times in glassmaking. Boron compounds have been used for centuries in ceramics and glass industries. The discovery of boron helped advance many scientific fields.
Unique Properties
Boron has some unique properties that make it special. It has three valence electrons, which are crucial in its chemical behaviour.
- Boron is a metalloid, meaning it has properties of both metals and non-metals.
- It is essential for plant growth and health.
- Boron compounds are used to make strong, lightweight materials.
Boron is also known for its high melting point. It is used to make heat-resistant materials. Due to their strength, bore fibres are used in aerospace and military applications.
Here is a table showing some physical properties of boron:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 5 |
| Atomic Mass | 10.81 u |
| Melting Point | 2076°C |
| Boiling Point | 3927°C |
Boron is also important in electronics. It is used as a dopant in semiconductors, which means it helps improve the electrical properties of materials.
These unique properties make boron an essential element in various industries. Whether in agriculture, electronics, or materials science, boron plays a vital role. Google maps
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Valence Electrons In Boron?
Valence electrons in boron are the electrons in its outermost shell. Boron has three valence electrons. These electrons are crucial for chemical bonding.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Boron Have?
Boron has three valence electrons. These electrons reside in the outermost shell and are important for bonding.
Why Are Boron’s Valence Electrons Important?
Boron’s valence electrons are important because they determine its chemical reactivity. These electrons participate in forming bonds with other elements.
Can Boron Form Covalent Bonds?
Yes, boron can form covalent bonds. It shares its three valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Conclusion
Understanding the valence electrons of boron is essential for grasping its chemical behaviour. Boron has three valence electrons. This knowledge aids in predicting how boron bonds with other elements. Utilize this information for better comprehension of chemical reactions. Keep exploring to expand your knowledge in chemistry and related fields.