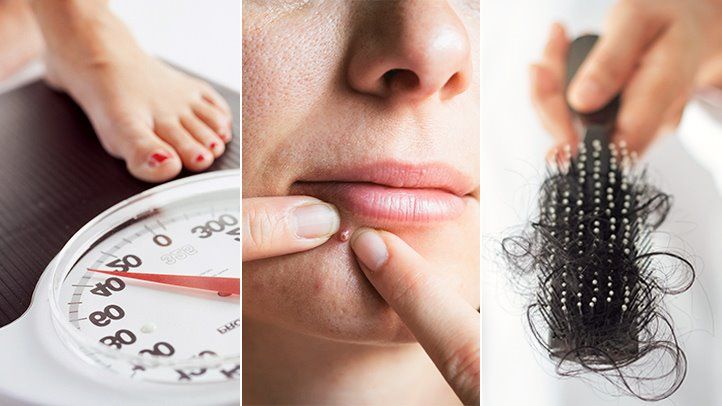
Early symptoms of PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease) include irregular menstrual cycles and excess androgen levels.
Early symptoms of PCOD, women may also experience weight gain and hair growth on the face and body. Short for Polycystic Ovary Disease, is a health condition that affects approximately 10% of women of childbearing age. It’s characterized by a hormonal imbalance and metabolism problems that can impact overall health and appearance. Identifying early symptoms of PCOD can be crucial for managing and preventing long-term complications.
If the patient can understand the early symptoms of PCOD, often diagnosed in women in their 20s or 30s, symptoms can occur as early as adolescence. Women with PCOD may struggle with issues related to fertility, as well as an increased risk of developing diabetes and heart disease. Despite the challenges it presents, many women successfully manage their symptoms with lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Recognizing these signs promptly can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Learn more about PCOS Treatment for Unmarried in the main guide
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, commonly known as PCOS, is a health condition that affects approximately 1 in 10 women of childbearing age. It is a complex endocrine disorder with a variety of symptoms that can impact not only a woman’s fertility but also her overall health and well-being. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for prompt management, which can help mitigate long-term risks like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Defining Pcos And Its Prevalence
PCOS is defined by a combination of symptoms and clinical signs rather than a single definitive test. It is marked by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen levels (male hormones typically present in women at lower levels), and polycystic ovaries. Its prevalence underscores the importance of awareness and understanding within the medical community and the general public.
Understanding The Hormonal Imbalance In Pcos
One of the hallmarks of PCOS is a hormonal imbalance. This involves elevated levels of androgens, or male hormones, which can lead to physical signs such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and sometimes male-pattern baldness. Women with PCOS often experience resistance to insulin, which can further exacerbate hormonal disturbances and impact metabolic health.
The Role Of Genetics And Environment In Pcos
While the exact cause of PCOS is undetermined, genetics and environmental factors play crucial roles. A family history of PCOS or related health issues can increase the risk, suggesting a genetic component. On the other hand, factors such as diet, lifestyle, and exposure to certain environmental toxins have been implicated in the development of the syndrome, pointing towards a multifaceted origin.
Early Warning Signs Of Pcos
Understanding the early warning signs of PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, can be pivotal in seeking timely medical intervention and managing the condition effectively. PCOS is a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age, and early indicators can often be subtle. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can help mitigate the risks of long-term health issues such as diabetes and heart disease.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: A Primary Indicator
One of the most apparent signs of PCOS is irregular menstrual cycles, also known as Oligomenorrhea in medical terms. This irregularity can manifest as prolonged cycles, fewer menstrual periods (less than eight in a year), or a complete absence of periods without pregnancy. These variations are typically a result of imbalances in reproductive hormones that disrupt the normal menstrual cycle.
When can you understand that it is irregular menstrual cycles? Irregular menstrual cycles break your normal menstrual periods. For this reason, the gap between them is less than 21 days or more than 35 days.
Hirsutism: Excessive Hair Growth And Its Causes
Hirsutism, characterized by unwanted, male-pattern hair growth in women, is another telltale sign of PCOS. Women may notice excessive hair on the face, chest, back, or abdomen. This symptom stems from increased levels of androgens, commonly known as male hormones, which are often elevated in women with PCOS.
Acne And Oily Skin: Hormonal Influences On The Skin
Acne breakouts, particularly when persistent and occurring beyond the teenage years, may be a signal of PCOS. The condition’s hormonal upheavals can lead to oily skin and severe acne, often resistant to over-the-counter treatments. This is attributable to the overproduction of androgens, which can cause oil glands to go into overdrive.
Thinning Hair On The Scalp: The Patterns And Reasons
Women with PCOS may also experience hair thinning or male-pattern baldness. This is due to the same androgens responsible for hirsutism, which can also cause the hair on the scalp to become thin and fall out. Recognizing this pattern of hair loss early can prompt important discussions with a healthcare provider.
Weight Gain And Difficulty Losing Weight: The Metabolic Tie-in
Many women with PCOS struggle with weight gain and a persistent challenge in losing weight. Insulin resistance is often associated with PCOS, which disrupts the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to weight gain and difficulty in shedding extra pounds. Understanding this metabolic tie-in is crucial for managing PCOS through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication.
Subclinical And Associated Conditions
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder with a spectrum of symptoms that can often evade early diagnosis. Diving into the realm of subclinical and associated conditions linked to PCOS can shed light on its nuanced early signs, which go beyond irregular menstrual cycles and hirsutism. Understanding these indicators can be vital for early intervention and management of the syndrome.
Insulin Resistance: Its Symptoms And Relation To Pcos
Insulin resistance, a condition where cells in the body do not respond effectively to insulin, is closely associated with PCOS. This inefficiency can lead to elevated blood glucose levels and a host of symptoms, including:
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Increased hunger, particularly for carbs
- Fatigue after meals
- Darkening of the skin, especially in creases and folds (acanthosis nigricans)
Individuals with PCOS frequently experience insulin resistance, which exacerbates PCOS symptoms and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Mood Changes And Mental Health: Identifying The Subtle Signs
Psychological disturbances may be early indicators of PCOS. Recognizing them is crucial for timely support and treatment. Here are subtle signs to watch out for:
- Mood swings or feelings of anxiousness without an apparent trigger
- Unexplained depression or bouts of lethargy
- Difficulty in concentration or cloudiness in the thought process
Comprehensive care for PCOS includes addressing these mental health subclinical signs, often overlooked in routine diagnostics.
Fertility Challenges: Understanding The Reproductive Impact
Many women first learn they have PCOS when they face difficulties conceiving. Fertility challenges arise due to anovulation, where the ovaries do not release an oocyte during a menstrual cycle. It is vital to be aware of symptoms like:
- Irregular periods or absence of menstruation
- Heavy or light menstrual flow
- Persistent acne or oily skin
These reproductive signs are crucial in predicting the presence of PCOS and demand a thorough evaluation to tailor the appropriate path for fertility treatment.
Sleep Disturbances: Links Between Pcos And Sleep Apnea
Women with PCOS are at increased risk for certain sleep disorders, including sleep apnea. Characteristics that may suggest the presence of sleep disturbances include:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Snoring, interrupted by pauses in breathing
- Insomnia or poor-quality sleep
Addressing sleep-related issues not only improves quality of life but also mitigates other PCOS symptoms.
Taking Action: When To See A Doctor And Diagnostic Tools
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, commonly known as PCOS, is a health condition that affects women of reproductive age. It is marked by a set of symptoms that can impact their hormonal balance, metabolism, and overall well-being. Understanding the early symptoms of PCOS is crucial for prompt intervention. Recognizing when these symptoms require a doctor’s attention and being informed about the available diagnostic tools is essential. With the right knowledge, women can seek timely medical help, ensuring better management of PCOS.
Recognizing The Threshold For Medical Intervention
Knowing whether to seek medical advice for PCOS starts by observing your body for potential warning signs. If you notice irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth on the face or body, significant weight gain, or difficulty getting pregnant, these could indicate that it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Persistent acne, oily skin, and scalp hair thinning shouldn’t be overlooked either. When lifestyle changes such as improved diet and exercise don’t alleviate these symptoms, booking a doctor’s appointment is the next critical step.
Diagnostic Criteria For Pcos: What To Expect From Your Doctor
At the doctor’s office, expect a comprehensive evaluation based on established diagnostic criteria for PCOS. Generally, physicians refer to the Rotterdam Criteria, which require at least two of the following three features to be present:
- Oligo-ovulation or anovulation – Irregular ovulation or lack thereof
- Hyperandrogenism – Elevated levels of masculinizing hormones
- Polycystic ovaries – Multiple cysts on the ovaries as detected by ultrasound
Your doctor may conduct various tests, including:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels
- A physical exam to check for signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance, and acne
- An ultrasound to examine your ovaries
Armed with these diagnostics, your healthcare provider can discern the presence of PCOS and advise a tailored treatment approach.
Emerging Research And Next Steps In Pcos Detection
Research in PCOS is ever-evolving, aiming to refine diagnostic methods and enhance early detection. Scientists are looking into genetic markers and other biomarkers that could lead to breakthroughs in how PCOS is understood and diagnosed. Future diagnostic tools may include advanced blood tests and imaging techniques to identify PCOS at its onset more accurately.
Keeping abreast with these developments is sensible as they promise more personalized and effective strategies in combating the effects of PCOS. If your symptoms align with PCOS, following these advancements and participating in discussions with your doctor regarding the most up-to-date diagnostic options is pertinent.
Frequently Asked Questions On Early Symptoms Of Pcod
What Are The First Stages Of Pcos?
Early stages of PCOS often present with irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain. These symptoms typically manifest during late adolescence or early adulthood.
How Early Do Pcos Symptoms Start?
PCOS symptoms can begin shortly after puberty, often during the teen years. Symptom onset typically occurs in early adulthood, around the ages of 20 to 30.
How Do You Know If A Girl Has Pcod?
A girl may have PCOD if she experiences irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain. Medical evaluation and diagnostics like ultrasound can confirm the condition.
At What Age Does Pcod Occur?
PCOD, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, typically manifests during adolescence or early adulthood, with most cases diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 30.
Conclusion
Understanding early PCOD symptoms enables timely action and effective management. Regular check-ups and lifestyle tweaks play key roles in controlling this condition. Remember, recognizing the signs early can significantly improve your health outcomes. Stay vigilant and consult healthcare professionals as needed.
Take charge of your well-being today. Google Maps
