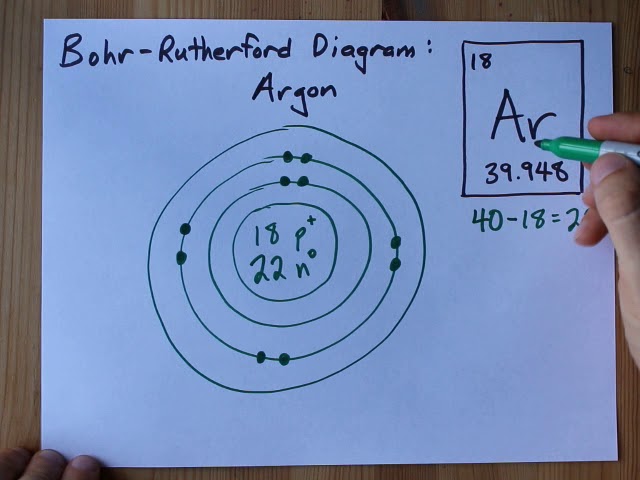
The electron configuration of Argon is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6. Argon has a total of 18 electrons.
Argon belongs to the noble gas family, which means that it has a full valence electron shell and is, therefore, unreactive. It is an element found in the periodic table with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. Its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6, indicating that it has 18 electrons organized into different energy levels.
Argon is a noble gas with a stable electron configuration and a full valence electron shell. This makes it unreactive and rarely forms chemical compounds. Its unreactive nature and inertness make Argon useful in various applications, such as filling incandescent light bulbs and creating a protective gas shield in welding processes. We will delve deeper into the electron configuration of Argon and explore its properties and significance in the world of chemistry.
The Basics Of Electron Configuration
Definition
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. It is often represented using a series of numbers and letters that denote the energy levels and sublevels where electrons are located.
Importance
Understanding electron configuration is crucial in predicting an element’s chemical properties and reactivity. It provides insights into an atom’s stability, bonding tendencies, and potential for forming chemical compounds.
An In-depth Look At Argon’s Electron Configuration
Are you ready to dive deep into the world of chemistry? In this blog post, we’ll examine argon’s electron configuration. Understanding how electrons are arranged within an atom is essential for comprehending the behavior and properties of different elements. By exploring argon’s electron configuration, we can gain insights into its stability and valence electrons, which play a crucial role in chemical reactions.
Orbital Diagram
Let’s start by examining argon’s orbital diagram. The orbital diagram visually represents how electrons occupy the various energy levels, or orbitals, within an atom. For argon (Ar), which has an atomic number of 18, the electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
We can break this down into individual orbital notations to make it easier to understand. The first two electrons occupy the 1s orbital, followed by the next two electrons in the 2s orbital. After that, the following six electrons fill the 2p orbital. Finally, the last eight electrons occupy the 3s and 3p orbitals.
Noble Gas Configuration
Argon belongs to the noble gas family, which includes elements known for their exceptional stability. These noble gases have completely filled electron shells, giving them little inclination to react with other components. In fact, argon’s electron configuration closely resembles that of its preceding noble gas, neon (Ne), except for two additional electrons in the 3p orbital. This configuration of a noble gas is often referred to as the “noble gas configuration.”
By having a noble gas configuration, argon possesses a full outer shell of electrons, making it highly stable and unreactive. This stability is why noble gases like argon are often used in applications where a non-reactive atmosphere is needed, such as in light bulb filaments and welding environments.
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom and are crucial for predicting how an element will interact with others in chemical reactions. For argon, its valence electrons are those in the 3s and 3p sub-levels. However, since argon has a complete octet (eight valence electrons), it has little to no tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons with other elements.
Having a full complement of valence electrons contributes to argon’s stability, making it difficult to form compounds with other elements. This lack of reactivity is a defining characteristic of noble gases, including argon.
In summary, argon’s electron configuration, with its noble gas configuration and complete outer shell of electrons, contributes to its stability and lack of reactivity. Understanding the electron configuration of elements allows us to predict their behavior and properties, providing valuable insights into the world of chemistry.
Frequently Asked Questions On Argon Electron Configuration
How Do You Write The Electron Configuration Of Argon?
The electron configuration of argon is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6.
What Element Is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2?
The element with the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 is Calcium (Ca).
What Element Has The Electron Configuration 1s22s22p63s23p2?
The electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p2 belongs to the element sulfur.
What Is The Electron Configuration Of 54?
The electron configuration 54 is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶.
Conclusion
Understanding the electron configuration of argon is crucial in chemistry. It dictates the element’s chemical properties and behavior. Scientists can predict its reactivity and bonding patterns by knowing how its electrons are arranged in energy levels. Researchers can develop new materials and understand various chemical processes with this knowledge.
Mastering the electron configuration of argon is vital for advancing the field of chemistry.