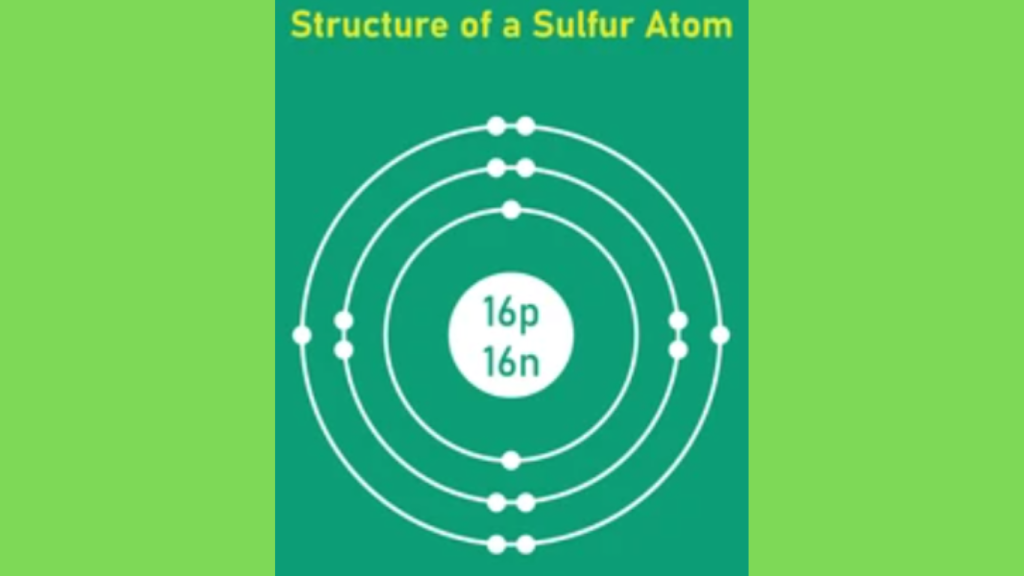
Now we discuss How Many Valence Electrons does S Have. Sulfur (S) has six valence electrons. It’s located in group 16 of the periodic table.
Sulfur, a non-metal element, is essential in various chemical processes. Found in group 16 of the periodic table, sulfur has an atomic number of 16. This places it in the same group as oxygen and selenium. With six valence electrons, sulfur forms essential compounds, including sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid.
These compounds are crucial in industries like fertilizer production, chemical synthesis, and even biological systems. Understanding sulfur’s valence electrons helps predict its chemical behavior and bonding patterns. Whether you’re a student or a professional, knowing these details about sulfur can enhance your grasp of chemistry fundamentals.
Sulfur In The Periodic Table
Sulfur is a fascinating element with unique properties. Understanding its position and characteristics in the periodic table helps in many fields. From chemistry to biology, sulfur plays a crucial role.
Position And Group
Sulfur is in the third period of the periodic table, meaning it has three electron shells. It belongs to the oxygen group, also known as group 16 or group VIA. Elements in this group share similar properties.
Elements in group 16 have six valence electrons. These electrons determine how an element reacts with others. Like its group members, sulfur tends to gain or share electrons in reactions.
Atomic Number And Symbol
Sulfur’s atomic number is 16, indicating it has 16 protons in its nucleus. The chemical symbol for sulfur is S, which is used in chemical equations and formulas.
The table below summarizes sulfur’s key information:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Group | 16 (VIA) |
| Period | 3 |
| Atomic Number | 16 |
| Symbol | S |
| Valence Electrons | 6 |
Knowing sulfur’s position in the periodic table helps predict its behavior and understand its bonding and reactions with other elements.
Valence Electrons Defined
Valence electrons are the electrons in an atom’s outer shell. They play a key role in chemical reactions, and understanding valence electrons helps us predict how atoms will bond.
Core Vs. Valence Electrons
Atoms have two types of electrons: core and valence.
- Core electrons are found in inner shells.
- Valence electrons are in the outermost shell.
The core electrons do not usually participate in chemical bonding. Valence electrons do participate in bonding.
Importance In Chemistry
Valence electrons determine an atom’s chemical properties.
They help in forming chemical bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons influences an element’s reactivity.
| Element | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 |
| Oxygen (O) | 6 |
| Sulfur (S) | 6 |
For example, sulfur (S) has six valence electrons. This makes sulfur reactive with many elements.
Sulfur’s Electron Configuration
Understanding sulfur’s electron configuration is vital in chemistry. Sulfur, symbolized as S, has an atomic number of 16, which means it has 16 electrons arranged in specific shells and sublevels.
Electron Shells
Electrons orbit the nucleus in regions called shells. Each shell can hold a certain number of electrons:
| Shell | Maximum Electrons |
|---|---|
| 1st | 2 |
| 2nd | 8 |
| 3rd | 18 |
For sulfur, the first shell holds 2 electrons, the second shell holds 8 electrons, and the third shell holds the remaining 6 electrons.
Filling Order
Electrons fill shells from the lowest energy level to the highest. This is known as the Aufbau principle. The sequence for sulfur is as follows:
- 1s2
- 2s2
- 2p6
- 3s2
- 3p4
This notation shows sulfur’s electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. The outermost shell, or valence shell, contains 6 electrons. These valence electrons are crucial for chemical bonding and reactions.

Determining Sulfur’s Valence Electrons
Understanding the valence electrons of sulfur (S) is vital in chemistry. Valence electrons help determine how elements bond and react.
Group 16 Elements
Sulfur is in Group 16 on the periodic table, also known as the chalcogens. Other elements in this group include oxygen, selenium, tellurium, and polonium.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | O | 8 |
| Sulfur | S | 16 |
| Selenium | Se | 34 |
| Tellurium | Te | 52 |
| Polonium | Po | 84 |
Valence Electron Count
Valence electrons are found in the outermost shell of an atom. For sulfur, this number is easy to determine.
- Look at sulfur’s position in Group 16.
- Elements in this group have six valence electrons.
So, sulfur has six valence electrons. These electrons play a key role in chemical bonding and reactions.
In summary, knowing sulfur’s valence electrons helps us understand its chemical behavior. This knowledge is essential for students and chemists alike.
Chemical Properties Of Sulfur
Sulfur is a fascinating element with a wide range of chemical properties. Found in the 16th group of the periodic table, sulfur has six valence electrons. These electrons play a crucial role in its reactivity and the formation of various compounds.
Reactivity
Sulfur is quite reactive, especially with metals and non-metals. It can form compounds with oxygen, hydrogen, and other elements. When sulfur reacts with oxygen, it forms sulfur dioxide (SO2), a significant compound in the atmosphere. Sulfur can also react with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gas with a distinct rotten egg smell.
- Reaction with Oxygen: Sulfur burns in oxygen to form sulfur dioxide.
- Reaction with Hydrogen: Sulfur reacts with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulfide.
- Reaction with Metals: Sulfur forms sulfides with metals, such as iron sulfide (FeS).
Common Compounds
Sulfur forms a variety of compounds that are essential in different industries. Below are some of the most common sulfur compounds:
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur Dioxide | SO2 | Used in the production of sulfuric acid |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | H2S | Used in the production of sulfuric acid |
| Sulfuric Acid | H2SO4 | Used in batteries and fertilizers |
| Iron Sulfide | FeS | Used in the production of iron and steel |
These compounds highlight sulfur’s versatility in various chemical reactions. Understanding sulfur’s chemical properties helps us appreciate its role in everyday applications.
Sulfur In Biological Systems
Sulfur is vital in biological systems. It plays a key role in various processes. Understanding how sulfur functions can help us grasp its importance.
Role In Proteins
Sulfur is essential in proteins. It is part of amino acids like cysteine and methionine, which are the building blocks of proteins. Sulfur helps maintain protein structure through disulfide bonds, which form bridges that stabilize protein shapes.
| Amino Acid | Role |
|---|---|
| Cysteine | Forms disulfide bonds |
| Methionine | Starts protein synthesis |
Without sulfur, proteins could not function properly. This would disrupt many biological processes.
Biochemical Pathways
Sulfur is crucial in biochemical pathways. It is part of coenzymes and vitamins, including coenzyme A, biotin, and thiamine. Coenzyme A is vital for energy production in cells.
- Coenzyme A – Energy production
- Biotin – Metabolizes fats and proteins
- Thiamine – Supports nerve function
Sulfur also helps detoxify the body. It is part of glutathione, an antioxidant that protects cells from damage and removes harmful substances from the body.
Industrial Applications Of Sulfur
Sulfur is a versatile element with many uses. Its industrial applications are broad and impactful. From producing crucial chemicals to enhancing materials, sulfur plays a key role in modern industry.
Sulfuric Acid Production
Sulfuric acid is one of the most important chemicals in the world. It is used in various industries for many purposes, and factories produce millions of tons of sulfuric acid yearly.
This acid is made from sulfur. The process involves burning sulfur to create sulfur dioxide. Then, sulfur dioxide is converted to sulfur trioxide. Finally, sulfur trioxide is dissolved in water to make sulfuric acid.
Industries use sulfuric acid to produce fertilizers. It also helps make phosphoric acid, which is vital for plant growth. The chemical industry uses sulfuric acid to create detergents, pigments, and explosives.
Vulcanization Of Rubber
Sulfur is crucial in making rubber more durable. This process is called vulcanization. It involves adding sulfur to rubber and heating it, making it stronger and more elastic.
Vulcanized rubber is used in many products. Car tires, shoe soles, and hoses all benefit from vulcanization, which makes rubber items last longer and perform better.
The discovery of vulcanization transformed industries. It enabled the creation of reliable and versatile rubber products.
Environmental Impact
The element sulfur (S) plays a significant role in the environment. Understanding how many valence electrons sulfur has is crucial for grasping its environmental impact. Sulfur’s chemical behavior affects many environmental processes.
Acid Rain
Sulfur contributes to the formation of acid rain. When sulfur dioxide (SO2) is released into the atmosphere, it reacts with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This acid then falls to the ground with rain, snow, or fog, harming plants, aquatic life, and infrastructure.
Acid rain can damage forests by leaching away essential nutrients from the soil. It also affects water bodies by lowering the pH, which harms fish and other aquatic organisms. Acid rain can corrode buildings and monuments, especially those made of limestone and marble.
Sulfur Emissions
Sulfur emissions are a major environmental concern. They primarily come from burning fossil fuels like coal and oil. Industrial processes, such as metal smelting and petroleum refining, also release sulfur compounds into the atmosphere.
| Source | Percentage of Total Emissions |
|---|---|
| Coal Burning | 60% |
| Oil Burning | 20% |
| Industrial Processes | 15% |
| Other Sources | 5% |
Reducing sulfur emissions is critical for improving air quality. Cleaner technologies and stricter regulations can help lower these emissions, which can mitigate the harmful effects of acid rain and improve overall environmental health.
Future Research
Future Research on the valence electrons of sulfur (S) is essential. It opens doors to new discoveries in chemistry and materials science. Two promising areas are Green Chemistry and Advanced Materials.
Green Chemistry
Green Chemistry focuses on creating eco-friendly processes and materials. Sulfur’s valence electrons play a key role here. Scientists study sulfur to develop greener chemical reactions.
- Reduce harmful by-products.
- Create renewable energy sources.
- Design biodegradable materials.
For example, sulfur compounds can help make cleaner batteries. These batteries are safer for the environment. By understanding sulfur’s valence electrons, we can innovate and protect our planet. Google maps
Advanced Materials
Advanced Materials research aims to create stronger, lighter, and more durable materials. Sulfur’s valence electrons are crucial in this field. They help in developing new materials with unique properties.
Here are some potential applications:
- Nanotechnology: Building tiny, powerful devices.
- Electronics: Enhancing the performance of circuits.
- Medicine: Creating better drug delivery systems.
By studying sulfur, scientists can push the boundaries of technology, leading to breakthroughs that can change our daily lives.
| Field | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Green Chemistry | Eco-friendly processes, renewable energy, biodegradable materials |
| Advanced Materials | Stronger materials, enhanced electronics, medical advancements |
Frequently Asked Questions About How Many Valence Electrons Does S Have
What Are Valence Electrons In Sulfur?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. Sulfur has six valence electrons. They determine how sulfur bonds with other elements.
How Do You Find Sulfur’s Valence Electrons?
To find sulfur’s valence electrons, look at its group number in the periodic table. Sulfur is in group 16, which means it has six valence electrons.
Why Are Valence Electrons Important In Sulfur?
Valence electrons are crucial because they determine sulfur’s chemical properties. They decide how sulfur reacts with other elements to form compounds.
How Does Sulfur’s Valence Electrons Affect Bonding?
Sulfur’s six valence electrons allow it to form multiple bonds. It can form double bonds with oxygen or single bonds with hydrogen.
Conclusion
Sulfur has six valence electrons, crucial for forming bonds and chemical reactions. Understanding this helps in various scientific and industrial applications. Knowing sulfur’s valence electrons aids in predicting its behavior in compounds. Stay curious and explore more about elements and their unique properties for deeper insights.