Treatment for osteoporosis often involves medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments.
Treatment for Osteoporosis starts Patients may take calcium, vitamin D, and prescribed medications to strengthen bones. a bone-thinning disease that affects millions globally, leading to fractures and reduced quality of life. Early detection and treatment are crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing complications. A rich vitamin D and calcium intake and weight-bearing exercises that stimulate bone growth are pivotal in preserving bone density.
In the treatment for osteoporosis, Physicians may prescribe bisphosphonates or other medication to slow bone loss and enhance bone mass. Ensuring a diet low in salt and high in fruits and vegetables also supports skeletal strength. Regular check-ups and bone density scans help monitor the condition’s progress, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment. Making these healthy lifestyle choices and following medical advice can manage osteoporosis effectively, reducing the risk of fractures and enhancing overall well-being.
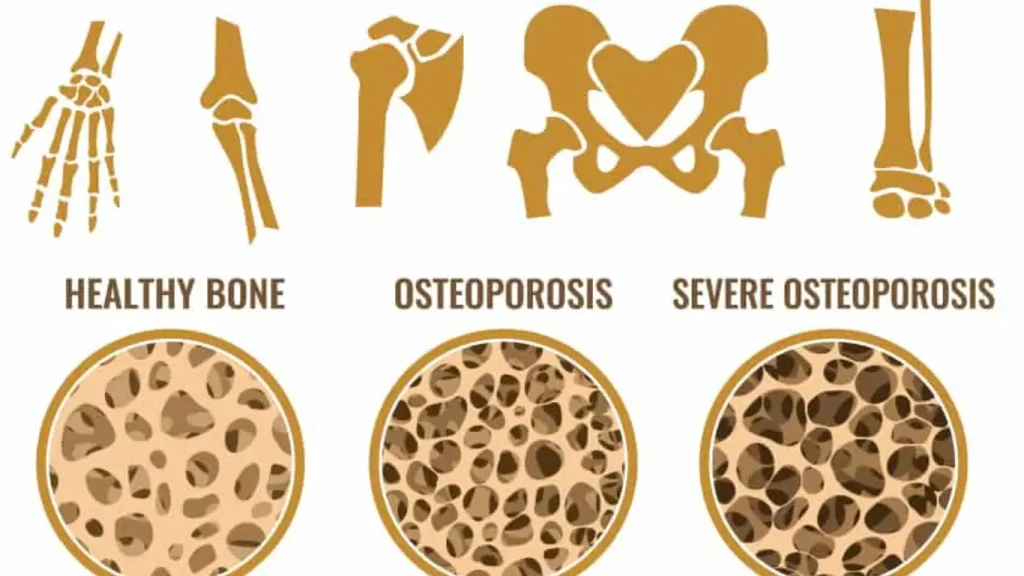
Understanding Osteoporosis
Learn more about the Ruptured Blood Vessel in Leg in the main guide.
Medical Interventions For Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, a silent stalker weakening bones from within, often remains undetected until a sudden fracture occurs. A strong medical intervention strategy is essential to manage this condition effectively. This section dives into current treatments, hormonal therapies, and innovative approaches emerging from ongoing clinical trials. It also highlights the supportive role of supplements like calcium and vitamin D. Understanding these options can be the key to maintaining bone health and preventing the potentially debilitating effects of osteoporosis.
Pharmacological Treatments
Bisphosphonates are usually the first line of defense, slowing bone loss and reducing fracture risk. Medications such as alendronate (Fosamax), ibandronate (Boniva), and zoledronic acid (Reclast) are common prescriptions.
Denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva) approaches the issue differently, targeting a specific protein involved in bone breakdown. Teriparatide (Forteo) and abaloparatide (Tymlos) encourage new bone growth but are typically reserved for those with severe osteoporosis due to their higher cost and potential side effects.
Healthcare providers should closely monitor these medications’ effectiveness, prescribed dosage, and possible side effects to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Bisphosphonates
What are bisphosphonates? Bisphosphonates are a group of drugs that work by slowing bone loss. They reduce the risk of hip and spine fractures. Bone renewal is a slow process, but in many people, an increase in bone density can be measured over five years of treatment.
Alendronate
Alendronate is used to prevent and treat osteoporosis (thinning of the bone) in women after menopause. This medicine may also increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis and in men and women to prevent and treat osteoporosis caused by long-term use of corticosteroids (cortisone-like medicine).
Ibandronate
Ibandronate is used to prevent and treat osteoporosis (a condition in which the bones become thin and weak and break easily) in women who have undergone menopause (”change of life,” end of menstrual periods).
Zoledronic acid
Zoledronic acid belongs to a class of drugs known as bisphosphonates. It lowers high blood calcium levels by reducing the amount of calcium released from your bones into your blood. It also works by slowing the breakdown of your bones by cancer to prevent bone fractures.
Denosumab
Denosumab is a bone anti-resorptive drug used to treat the following FDA-approved indications: Prevention of skeletal-related events: Denosumab is indicated for bone pain and fractures secondary to multiple myeloma or bone metastases from solid tumors.
Teriparatide
Teriparatide is a medication used to manage and treat osteoporosis. It is in the anabolic class of osteoporosis medications. Human parathyroid hormone is a powerful osteoanabolic agent made up of the first 34 amino acids of the N-terminal.
Abaloparatide
Abaloparatide, a synthetic peptide analog of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP), is used to manage and treat osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone mineral density due to changes in bone microstructure, resulting in an elevated risk of fractures.
Hormone Therapy And Its Controversies
Hormone therapy has been a controversial topic. While Estrogen Replacement Therapy (ERT) and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) such as raloxifene can help maintain bone density, they come with risks. Concerns over the association of hormone therapy with increased risks of breast cancer, heart disease, and blood clots have led to a more cautious prescription of these treatments. Calcitonin, another hormone used in treatment, has shown efficacy, particularly in spinal fracture pain reduction, but it is generally considered less effective in bone density improvement than other treatments.
Emerging Drug Therapies And Clinical Trials
Excitement is building in the field of osteoporosis treatment as new pharmacological advances emerge. Odanacatib, an inhibitor of the enzyme cathepsin K, has shown promising results in maintaining bone density. Additionally, romosozumab, which both increases bone formation and decreases bone resorption, is under investigation. Sclerostin inhibitors, harnessing a novel approach to bone health, are also gaining significant attention. Clinical trials are critical to developing these emerging therapies, where safety and effectiveness are rigorously tested before FDA approval and widespread availability.
Odanacatib
Odanacatib is an investigational treatment for osteoporosis and bone metastasis. It is an inhibitor of cathepsin K, an enzyme involved in bone resorption.
Romosozumab
Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody sclerostin inhibitor that is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at an increased risk of fracture. This anabolic medication stimulates bone formation while suppressing bone resorption.
Role Of Supplements: Calcium And Vitamin D
Supplementing with calcium and vitamin D is often recommended to support bone health. Calcium is the cornerstone of strong bones, while vitamin D is critical in calcium absorption and bone growth.
Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs) for calcium and vitamin D vary by age, sex, and other factors. Adequate intake is crucial, but excessive consumption has its pitfalls and should be avoided. Dietary sources are preferred, but supplements can help fill nutritional gaps when necessary. Regular blood tests can determine if the levels are within the optimal range for bone health maintenance.
| Supplement | Function | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Bone strength and density | 1000-1200 mg/day |
| Vitamin D | Calcium absorption, bone growth | 600-800 IU/day |
The Side Effects of Treatment for Osteoporosis
Treatment for osteoporosis typically aims to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures, but like any medical intervention, it can have side effects. The specific side effects depend on the type of treatment, which may include medications, lifestyle changes, or supplements. Here’s an overview of common osteoporosis treatments and their potential side effects:
1. Bisphosphonates
How they work, Slow bone breakdown, increasing bone density.
Common side effects:
- Gastrointestinal issues: nausea, heartburn, or ulcers.
Bone, joint, or muscle pain.
Flu-like symptoms after IV administration.
Rare side effects:
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw (jawbone deterioration).
Atypical femur fractures (rare but serious).
2. Denosumab (Prolia)
It works by inhibiting bone resorption and increasing bone mass.
Common side effects:
- Back pain, muscle pain.
High cholesterol.
Urinary tract infections.
Rare side effects:
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Atypical femur fractures.
Increased risk of infections due to immune suppression.
3. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
Examples: Raloxifene (Evista)
How they work, Mimic estrogen positively affects bone density without affecting other tissues.
Common side effects:
- Hot flashes.
Leg cramps.
Rare side effects:
Increased risk of blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism).
4. Parathyroid Hormone Analogues
Examples: Teriparatide (Forteo), Abaloparatide (Tymlos)
They work by Stimulating new bone formation by acting like parathyroid hormones.
Common side effects:
- Nausea, dizziness.
- Leg cramps.
Rare side effects:
- Increased risk of osteosarcoma (a type of bone cancer) with prolonged use.
5. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
It works by Replacing estrogen lost during menopause to help maintain bone density.
Common side effects:
- Breast tenderness, bloating.
Mood swings.
Rare side effects:
- Increased risk of breast cancer, stroke, heart disease, and blood clots.
6. Calcitonin
It works by Slowing bone loss and may relieve bone pain in cases of osteoporosis.
Common side effects:
- Nasal irritation (with nasal spray).
Flushing, nausea (with injections).
Rare side effects:
Possible increased risk of cancer (in long-term use).
7. Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements
They work to support bone health by ensuring adequate calcium levels and improving calcium absorption.
Common side effects:
- Constipation.
Gas or bloating.
Rare side effects
- Kidney stones (if taken in excess).
8. Romosozumab (Evenity)
It works by stimulating bone formation and decreasing bone resorption.
Common side effects:
- Joint pain.
Headache.
Rare side effects:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular events (heart attack, stroke).
General Considerations:
Lifestyle side effects:
Dietary changes or physical exercises recommended for osteoporosis management rarely cause side effects but can result in muscle soreness or discomfort.
Medication interactions:
Osteoporosis medications may interact with other medications, so monitoring any new symptoms is essential.
Regular monitoring and consultations with a healthcare provider can help manage or prevent side effects while optimizing treatment outcomes.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies For Osteoporosis Management
Osteoporosis, characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures, can be intimidating, but incorporating simple lifestyle and home remedies can significantly bolster bone health. These strategies complement medical treatments, empowering individuals to take charge of their bone density through everyday actions. From dietary adjustments to targeted exercise programs, let’s explore practical steps you can take to manage osteoporosis from the comfort of your home.
Dietary Recommendations
Your diet plays a pivotal role in bone health. Calcium and vitamin D are the cornerstones of strong bones. Here are dietary recommendations to boost your bone strength:
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent calcium sources.
- Leafy greens: Incorporate spinach, kale, and broccoli into your meals.
- Fortified foods: Look for cereals, juices, and milk alternatives fortified with calcium and vitamin D.
- Protein: Adequate protein from sources like lean meats, beans, and nuts is essential for bone repair and strength.
- Fruits and vegetables: A colorful variety provides the micronutrients necessary for maintaining bone health.
Incorporate these into your diet, but consult a healthcare professional to personalize your nutritional plan.
Exercise Programs For Bone Health
An exercise regimen tailored to bone health can work wonders. Weight-bearing and resistance exercises stimulate bone formation and slow deterioration. Tailor your fitness routine to include:
- Walking, hiking, or jogging
- Strength training with weights or resistance bands
- Balance exercises such as yoga or Pilates
- Low-impact aerobics
Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week, but consult a physical therapist to create a safe and effective program that matches your needs.
Preventing Falls And Fractures At Home
To minimize the risk of falls and fractures, transform your living space into a safety zone with these tips:
- Secure loose rugs and eliminate trip hazards.
- Ensure ample lighting, especially in stairways and hallways.
- Install grab bars and handrails in critical areas like the bathroom and alongside stairs.
- Wear non-slip footwear both indoors and outdoors.
Regular vision check-ups and a clutter-free home environment also play a critical role in preventing accidents.
Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture And Tai Chi
Alternative therapies can complement conventional treatments. Two practices that show promise for osteoporosis include:
- Acupuncture: This ancient technique may help manage pain and improve mobility.
- Tai Chi: A gentle form of martial arts known for enhancing balance and muscle strength, potentially reducing fall risk.
Both therapies warrant discussion with your physician to ensure they fit within your overall management plan.
Monitoring Bone Density And Ongoing Care
Consistent monitoring of bone density through tests like the DEXA scan is crucial for understanding the progression of osteoporosis. Establish a schedule for these screenings in consultation with your healthcare team, and adhere to any prescribed medication regimen. Ongoing care will likely include periodic reviews of your diet, exercise, and lifestyle practices to ensure optimal bone health maintenance. Google Maps
The Future Of Osteoporosis Treatment
The quest for stronger bones does not end here. As we gaze into the realm of medical possibilities, the future of osteoporosis treatment shines with innovative therapies and ground-breaking research. Emerging technologies and scientific discoveries promise to revolutionize how we prevent and manage this widespread condition. Let’s dive into the tantalizing prospects that are shaping a new horizon for osteoporosis treatment.

Advancements In Bone Densitometry
Thanks to advancements in bone densitometry, measuring bone strength is becoming more refined and precise. The latest methods provide detailed 3D images, offering unparalleled bone quality and integrity insights. These enhanced techniques are set to improve the accuracy of osteoporosis diagnosis, allowing for earlier and more targeted interventions.
- High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT)
- Trabecular bone score (TBS)
- 3D modeling of bone density and structure
Genetic Research And Personalized Medicine
Unlocking the genetic codes contributing to bone health is forging the path to personalized medicine. Scientists are identifying genetic markers that could predict an individual’s risk for osteoporosis and fracture susceptibility. This information is crucial in tailoring prevention strategies and treatments to each patient’s unique genetic makeup.
- Identification of genetic risk factors
- Development of personalized treatment plans
- Increased effectiveness of prevention strategies
The Role Of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is a beacon of hope in the regeneration of bone tissue. Researchers are examining the potential of stem cells to promote bone healing and restore bone density. This cutting-edge approach might offer a solution for those who do not respond to current treatments; positioning stem cell therapy as a game-changer in the fight against osteoporosis.
| Stem Cell Type | Potential Application |
|---|---|
| Mesenchymal Stem Cells | Bone regeneration and repair |
| Adipose-derived Stem Cells | Support of new bone growth |
Public Health Strategies To Reduce Incidence
Public health strategies are instrumental in reducing the incidence of osteoporosis. Emphasis on education, nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments will be the cornerstones of future efforts. Initiatives to increase awareness and promote bone-healthy habits can substantially lower the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures globally.
- Nationwide educational campaigns
- Improved dietary guidelines for bone health
- Community-based exercise programs
Frequently Asked Questions Of Treatment For Osteoporosis
What Is The Fastest Way To Increase Bone Density?
Engage in weight-bearing exercises and consume calcium-rich foods and vitamin D. Consult a doctor about possible bone density medication.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Person With Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis does not directly affect life expectancy. However, associated fractures, particularly hip fractures, can cause complications that decrease lifespan. Proper management can reduce risks and improve quality of life.
Does Osteoporosis Get Worse Without Treatment?
Osteoporosis generally progresses when left untreated, leading to increased bone fragility and a higher risk of fractures. Regular medical evaluation and appropriate therapy can help manage symptoms and slow the disease’s progression.
What Not To Do If You Have Osteoporosis?
Avoid high-impact exercises that increase fracture risk. Don’t smoke or consume excessive alcohol. Refrain from bending forward from the waist or twisting the spine excessively. Limit lifting heavy objects. Steer clear of medications that could weaken bones.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis treatment requires a proactive approach. Adopting healthy habits, such as good nutrition and regular exercise, is essential. Medications and lifestyle changes work together to strengthen bones. Consulting healthcare providers ensures personalized treatment plans. Remember, early intervention may lead to better outcomes in managing this silent disease.
