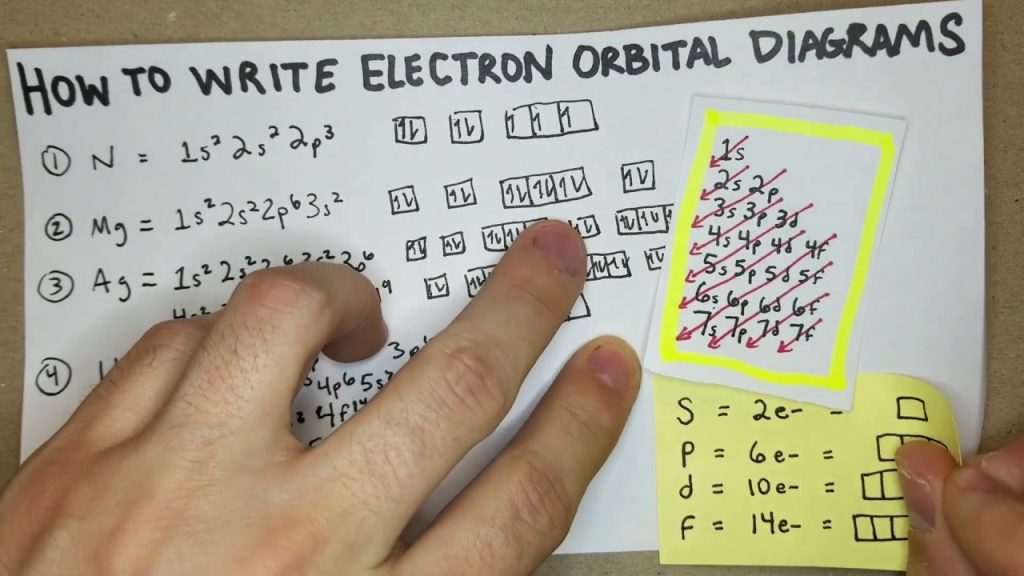
An electron configuration is a shorthand way of representing the distribution of electrons in an atom. At the same time, an orbital filling diagram provides a visual representation of the placement of electrons in specific orbitals of an atom. Understanding the arrangement of electrons within an atom is crucial for understanding its chemical properties.
Electron configuration and orbital filling diagrams both serve as tools for visualizing the distribution of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. While electron configuration is written in a specific format using numbers and letters to denote the energy levels and sublevels of electrons, an orbital filling diagram uses arrows to represent the spin and placement of electrons within each orbital.
Both methods are essential for comprehending the behavior of atoms and their interactions in chemical reactions. Let’s explore the differences between these two concepts to gain a deeper understanding of atomic structure.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is often expressed using the principal quantum number and the sublevel designation. This arrangement provides a detailed understanding of an element’s electron distribution within its energy levels. Let’s explore electron configuration in greater detail.
Representation Of Electron Distribution
In electron configuration, the arrangement of electrons is represented using a series of numbers and letters, reflecting the energy levels, sublevels, and the number of electrons within them. This representation gives a clear depiction of the distribution of electrons within an atom.
Utilization Of Sublevels And Orbitals
Electron configuration utilizes sublevels and orbitals to specify the precise location of electrons within an atom. This method provides intricate details about the distribution of electrons, enabling scientists and researchers to comprehend an element’s properties and behavior more comprehensively.
Orbital Filling Diagram
In chemistry, understanding how electrons are distributed within an atom is essential. This distribution is represented using two methods: electron configuration and orbital filling diagram. While electron configuration outlines the specific arrangement of electrons within different energy levels and orbitals, the orbital filling diagram provides a visual representation of how these electrons occupy the atom’s orbitals. Let’s delve deeper into the orbital filling diagram to understand better how it illustrates electron occupation.
Visual Representation Of Electron Occupation
The orbital filling diagram is a graphical representation that allows us to visualize the different energy levels and orbitals in an atom, as well as the number of electrons present in each orbital. This diagram employs a color-coded scheme to indicate the electron occupation of each orbital, making it easier to grasp at a glance.
-
The diagram starts with the lowest energy level, known as the 1s orbital. This orbital can accommodate only two electrons.
-
The second energy level includes both the 2s and 2p orbitals. The 2s orbital can also accommodate two electrons, while the 2p orbital can hold up to six electrons.
-
Continuing with this pattern, the higher energy levels can accommodate more and more electrons, as per the respective orbital’s capacity.
By visualizing the electron occupation in this manner, it becomes easier to comprehend the distribution of electrons among the different orbitals and energy levels within an atom.
Depiction Of Energy Levels
The orbital filling diagram not only illustrates the electron occupation but also helps depict an atom’s energy levels. In this diagram, the energy levels are represented by horizontal lines or boxes, with each line representing a different energy level. The lowest energy level appears at the bottom, followed by subsequent upward levels.
The diagram follows the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher ones. This principle is clearly depicted in the orbital filling diagram, as the electrons fill the energy levels in sequential order, starting from the 1s orbital, then moving to the 2s and 2p orbitals, and so on. This sequential filling pattern helps organize and understand an atom’s electron distribution.
The orbital filling diagram effectively portrays the electron occupation and energy distribution within an atom by utilizing both color coding and a sequential representation of energy levels. This visual representation simplifies comprehension and aids in the study of electron configurations.
Key Differences
Understanding the arrangement of electrons within an atom is essential in chemistry and atomic theory. Two commonly used methods to represent this arrangement are electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams. While both techniques provide valuable insights into the distribution of electrons, they differ significantly in terms of format and notation, as well as the level of detail they offer. Let’s delve deeper into these key differences.
Format And Notation
Electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams have distinct characteristics regarding format and notation. In electron configurations, the arrangement of electrons is indicated by a numerical code representing the different energy levels, sublevels, and orbitals. Each number denotes the principal energy level, while a letter represents the sublevel or type of orbital, such as s, p, d, or f.
On the other hand, orbital filling diagrams visually illustrate the distribution of electrons using boxes or circles to represent orbitals. Each orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons, which are represented by arrows indicating their spin. Unlike electron configurations, orbital filling diagrams make it easier to visualize the overall electron distribution within an atom.
Level Of Detail
While both electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams provide information about the electron distribution, they differ in terms of the level of detail they offer. Electron configurations offer a more comprehensive representation of the electron arrangement, providing information about the specific sublevels and orbitals occupied by electrons within each energy level. This allows scientists to determine the precise location of each electron within an atom.
On the other hand, orbital filling diagrams focus more on the overall electron configuration rather than the specific details. They provide a simplified visual representation, emphasizing the number of electrons within each energy level and sublevel rather than their precise orbital locations. This makes orbital filling diagrams more accessible and easier to interpret, especially for those with limited chemistry knowledge.
Overall, while electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams serve the same purpose of illustrating electron distribution, they differ in format, notation, and level of detail. Electron configurations offer a more detailed and comprehensive representation, while orbital filling diagrams provide a simplified visual overview. Both methods are valuable tools for understanding the arrangement of electrons within an atom and contribute to our understanding of the fascinating world of atomic theory.
When To Use Which
Understanding electron configuration and orbital filling diagrams is essential for comprehending the intricate behavior of atoms and their interactions in chemical reactions. Knowing when to utilize each representation is crucial for applying it effectively in practical scenarios in chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Practical Scenarios In Chemistry
The electron configuration notation is generally used to explain the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s energy levels and sublevels when dealing with chemical bonding and the formation of compounds. It offers a concise and systematic way to depict the distribution of electrons among different orbitals within an atom.
On the other hand, orbital filling diagrams are particularly useful when visualizing and understanding the electron affinities of elements, especially regarding the filling of orbitals during various chemical reactions and the determination of an element’s chemical properties.
Application In Quantum Mechanics
When delving into the intricacies of quantum mechanics, such as analyzing atomic spectra and quantizing energy levels, electron configuration notation is often preferred due to its ability to convey the specific arrangement of electrons within an atom’s orbitals, providing insights into the behavior of atoms at the quantum level.
In contrast, orbital filling diagrams are frequently employed to relate quantum numbers and orbital energies, aiding in the visualization and understanding of the positioning and occupancy of electrons across different orbitals as dictated by the laws of quantum mechanics.
Examples
Examples:
Electron Configuration Demonstration
An electron configuration shows the distribution of electrons in an atom’s energy levels.
Example:
-
Hydrogen: 1s1
-
Carbon: 1s2 2s2 2p2
-
Oxygen: 1s2 2s2 2p4
Orbital Filling Diagram Illustration
An orbital filling diagram visually represents how electrons fill specific orbitals in an atom.
Example:
|
Orbital |
Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
|
1s |
↑ |
|
2s |
↑ ↑ |
|
2p |
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ |
Benefits And Limitations
Benefits and Limitations:
Understanding the difference between electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams is critical in chemistry. Let’s explore the benefits and limitations of each representation.
Advantages Of Each Representation
-
Electron Configuration provides a concise way to represent the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
-
Orbital Filling Diagrams offer a visual representation of the energy levels and orbitals occupied by electrons.
Challenges In Real-life Situations
-
Electron Configuration: Limited visual aids can make it challenging for some learners to grasp the concept.
-
Orbital Filling Diagrams: The complex nature may lead to confusion when dealing with transition metals.
Both representations have advantages and challenges, making it essential to understand and use the differences appropriately.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Difference Between An Electron Configuration And An Orbital Filling Diagram
What Is An Electron Configuration?
An electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s energy levels. It specifies the number of electrons at each energy level and orbit.
What Is An Orbital Filling Diagram?
An orbital filling diagram illustrates the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. It shows the sequential filling of orbitals based on electron spin and energy levels.
How Do Electron Configurations Differ From Orbital Filling Diagrams?
While both describe electron distribution, electron configurations detail the specific number of electrons in each orbital and energy level, whereas orbital filling diagrams visually represent the electron distribution in orbitals.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams is crucial in comprehending the arrangement of electrons in an atom. While electron configurations depict the distribution of electrons in energy levels and sublevels, orbital filling diagrams provide a visual representation of the specific orbitals containing electrons.
Both these tools aid in predicting an atom’s chemical properties and behavior. Mastering these concepts paves the way for a deeper understanding of atomic structure and the periodic table.